Launching a new business can be an exciting, yet daunting, endeavor. One of the most critical steps before taking the plunge is to validate your business idea. This process involves rigorously testing the feasibility and market demand for your product or service, saving you valuable time, resources, and potential heartache down the road. Validating your business idea provides crucial insights into your target audience, their needs, and their willingness to pay for what you offer. Through thorough validation, you can mitigate risks, refine your business model, and increase your chances of success.
This article explores the essential steps to effectively validate your business idea before launching. We will delve into proven strategies for market research, including analyzing your target audience, assessing the competitive landscape, and conducting thorough product testing. Learn how to gather valuable feedback and iterate on your initial concept to create a product or service that truly resonates with your target market. By following these guidelines, you can transform your promising idea into a thriving and sustainable business.
Why Validation Is Crucial
Validating your business idea is essential before launching. It significantly reduces the risk of failure by confirming market demand and identifying potential problems early on. This saves you valuable time, money, and resources that could be wasted on an unviable venture.
Validation provides critical insights into your target audience, allowing you to refine your product or service to meet their specific needs and preferences. This increases the likelihood of achieving product-market fit, a key determinant of long-term success.
Conducting Market Research
Market research is a critical step in validating your business idea. It helps you understand your target market, competition, and the overall market landscape. This information allows you to refine your business strategy and reduce the risk of failure.
Key areas to research include:
- Target Audience: Identify their demographics, needs, and preferences.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze your competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
- Market Size and Trends: Determine the overall market size and identify any emerging trends.
Effective market research methods include surveys, interviews, and analyzing industry reports.
Identifying Customer Pain Points
A crucial step in validating your business idea is identifying customer pain points. This involves understanding the problems and frustrations your target market experiences related to your proposed product or service. By addressing these pain points effectively, you increase the likelihood of your business succeeding.
Begin by clearly defining your target market. Once you know who your ideal customer is, you can begin researching their needs and challenges. Effective methods for gathering this information include surveys, interviews, and analyzing online forums and social media discussions.
Focus on uncovering unmet needs. These are areas where current solutions fall short or where no solutions exist. Identifying these gaps presents opportunities for your business to offer unique value and differentiate itself from competitors.
Running Small-Scale Tests
After formulating your hypotheses, the next crucial step is to conduct small-scale tests. These tests provide valuable data to validate your assumptions and mitigate risk before a full launch. Small-scale testing allows you to gather feedback, identify potential problems, and refine your business idea in a controlled environment.
Several methods exist for conducting these tests. Consider surveys to gauge customer interest and gather demographic data. Pre-selling or crowdfunding campaigns can assess market demand and generate early revenue. Landing pages coupled with targeted advertising can measure click-through rates and conversion metrics. Finally, running pilot programs with a small group of users provides real-world feedback on your product or service.
Pre-Selling or Crowdfunding

Pre-selling and crowdfunding are powerful methods for validating a business idea before a full launch. They allow you to gauge market interest and gather valuable feedback directly from potential customers.
Pre-selling involves offering your product or service for sale before it’s actually available. This can be done through a landing page, email list, or even pre-orders on an e-commerce platform. Success in pre-selling demonstrates a clear demand and can even generate initial capital.
Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo provide a structured way to present your idea to a larger audience and solicit funding. Reaching your funding goal serves as strong validation, while falling short can indicate a need to refine your offering or target market.
Collecting Honest Feedback
Gathering feedback is crucial for validating your business idea. Honest feedback, however, can be difficult to obtain. People may be hesitant to criticize, especially if they know you personally.
Target the right audience. Seek feedback from your target demographic. Feedback from individuals outside your target market may not be relevant.
Ask specific questions. Instead of asking general questions like “Do you like this idea?”, ask specific questions such as “What do you think of this pricing model?” or “Would you use this product/service and why?”.
Use various methods. Consider surveys, interviews, and focus groups. Each method offers unique advantages for gathering different types of information.
Remain objective. Don’t get defensive about negative feedback. View it as an opportunity to improve your business idea.
Analyzing Competitor Landscape
A crucial step in validating your business idea is analyzing the existing competitor landscape. This involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors to understand the existing market dynamics.
Research your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. What are they doing well? Where are they falling short? This analysis can reveal potential opportunities for your business to differentiate itself and offer unique value to customers.
Examine their pricing strategies, marketing efforts, and target audience. Understanding these aspects can help you refine your own business strategy and position yourself effectively in the market.
Avoiding Confirmation Bias
Confirmation bias is a significant hurdle in objectively evaluating business ideas. It’s the tendency to favor information that confirms pre-existing beliefs and dismiss information that contradicts them. This can lead to launching products or services nobody wants.
To mitigate confirmation bias, actively seek out disconfirming evidence. Don’t just ask friends and family; they’re likely to support you regardless. Instead, engage with your target market directly.
Conduct thorough market research using surveys, interviews, and competitive analysis. Ask challenging questions that probe potential weaknesses in your idea. Be open to negative feedback and use it to refine or even pivot your business idea.
Refining the Business Concept
Once you’ve gathered feedback and analyzed the market, it’s time to refine your initial business concept. This crucial step involves incorporating the insights gained from your validation efforts. This might mean adjusting your target audience, tweaking your product or service offering, or revising your marketing strategy.
Key areas to focus on during the refinement process include value proposition, competitive differentiation, and revenue model. Ensure your value proposition clearly articulates the benefits customers receive. Sharpen your competitive differentiation to highlight what sets you apart from existing solutions. Finally, solidify your revenue model to ensure its sustainability and profitability.
Deciding to Pivot or Proceed
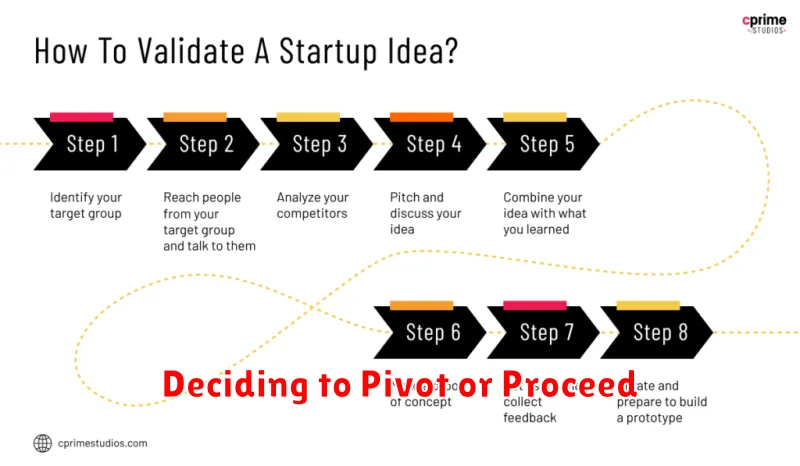
After gathering and analyzing data, the crucial decision of whether to pivot or proceed arises. A positive validation, where your idea resonates with the target market and demonstrates potential profitability, signals a green light to proceed.
Conversely, negative validation doesn’t necessarily equate to failure. It provides valuable insights, highlighting areas needing adjustment. This juncture requires careful consideration: Should you pivot by modifying your initial idea based on the feedback received? Or, if the data reveals fundamental flaws, should you proceed with an entirely different approach?

