Launching a successful business hinges on choosing the right business model. A business model is the framework that outlines how your business will create, deliver, and capture value. This encompasses everything from your target market and value proposition to your revenue streams and cost structure. Making the right choice from the outset is critical for long-term sustainability and profitability. This article will guide you through the key considerations and steps involved in selecting the optimal business model for your specific business idea. Understanding the various types of business models available, such as subscription models, freemium models, advertising models, and affiliate marketing, will be crucial to your success. Proper business model selection is the foundation upon which you will build your business.
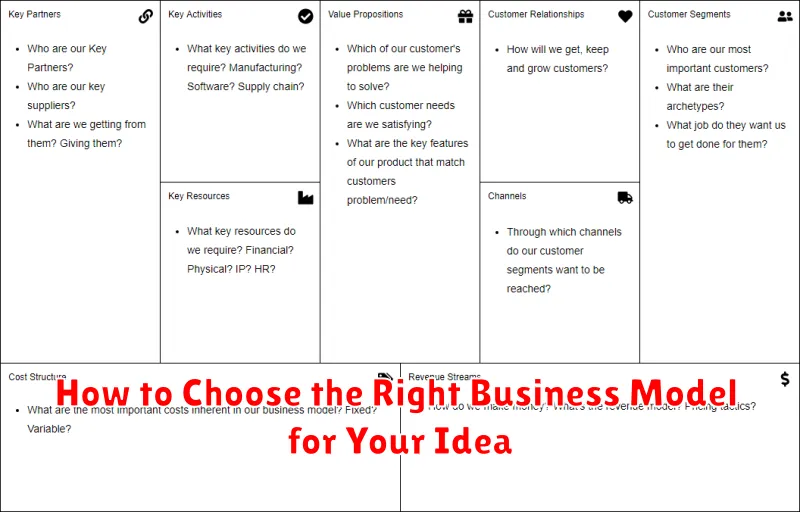
Identifying the most appropriate business model requires careful evaluation of your business idea and its alignment with market demands. Factors to consider include your target audience, competitive landscape, revenue generation strategies, and resource allocation. Whether you’re starting a small business or launching a startup, the business model canvas can be an invaluable tool for visualizing and analyzing your business model. This article will provide a practical framework for navigating the complexities of business model selection, empowering you to make informed decisions that position your business for success. Choosing the right business model is not just about making money; it’s about building a sustainable enterprise that delivers value to your customers and achieves your business goals.
What Is a Business Model?
A business model describes how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value. It’s a plan for how a company will generate revenue and profit. It outlines the key components of the business, including the products or services offered, the target market, the key activities, and the cost structure.
A strong business model is essential for any successful business. It provides a framework for making decisions and helps to ensure that the business is sustainable in the long term. It is not simply about making a profit; it’s about how a company creates and delivers value to its customers while also generating revenue to cover its costs and achieve its objectives.
Popular Models: Product, Service, Subscription
Several established business models offer proven frameworks for success. Understanding their core components is crucial for selecting the right fit.
Product Model
This model focuses on the creation and sale of tangible goods. Key activities include manufacturing, distribution, and retail. Profitability relies on efficient production and effective marketing to drive sales volume.
Service Model
Service models center on providing intangible value to customers. This could range from consulting and education to repairs and entertainment. Success hinges on expertise, customer service, and building strong client relationships.
Subscription Model
Subscription models offer recurring access to a product or service in exchange for regular payments. This model prioritizes customer retention and predictable revenue streams. Key metrics include churn rate and customer lifetime value.
Freemium, Licensing, and Affiliate Models
These models offer diverse approaches to monetizing your idea. Freemium provides a basic service for free, enticing users to upgrade for premium features. This model relies on a large user base and a compelling premium offering.
Licensing involves granting others the right to use your intellectual property, such as technology or designs, in exchange for fees. This can generate passive income but requires strong IP protection.
Affiliate marketing focuses on promoting other businesses’ products or services and earning a commission on resulting sales. This model leverages existing audiences and requires effective marketing strategies.
Marketplace and Platform-Based Ideas
Marketplace business models facilitate transactions between buyers and sellers. A key characteristic is that the platform itself doesn’t own the inventory. Instead, it connects supply and demand, taking a commission or fee on each transaction. Examples include Etsy for handmade goods and Airbnb for lodging.
Platform businesses create an ecosystem where different groups interact and create value. These platforms often provide tools, resources, or infrastructure that support this interaction. Think of video game consoles like PlayStation or Xbox, where developers create games for users to play. The platform provider benefits from sales of both hardware and software.
Pros and Cons of Each Model
Evaluating business models requires careful consideration of their advantages and disadvantages. A subscription model offers predictable recurring revenue, fostering customer loyalty. However, it demands continuous value delivery and can face churn. Freemium models attract a large user base, converting some to paying customers. The challenge lies in balancing free features with premium offerings and managing acquisition costs.
Advertising-based models generate revenue through ad placements, potentially reaching a vast audience. However, ad revenue can fluctuate and user experience can be compromised by intrusive ads. Transaction-based models generate revenue with each sale, offering clear revenue streams. The challenge is maintaining sales volume and managing transaction costs.
Matching Model to Market Needs
A crucial step in choosing the right business model is ensuring it aligns with market needs. Market analysis is essential. Understand your target audience’s pain points, preferences, and purchasing behavior.
Consider whether your proposed model effectively addresses a genuine market need. Does it offer a unique value proposition? Analyze your competitors. How does your model differentiate itself and offer something better or different?
Finally, evaluate the feasibility of your model in the current market landscape. Are there any regulatory hurdles or logistical challenges? Can you reach your target customers effectively? Answering these questions ensures your chosen business model is not only innovative but also viable.
Understanding Revenue Streams
A crucial aspect of choosing the right business model is understanding how it will generate revenue. A revenue stream represents the various ways your business earns money from selling its products or services.
Identifying your potential revenue streams is essential. Consider whether you’ll rely on direct sales, subscriptions, advertising, licensing, or other methods. Clearly defining your revenue streams early on helps project profitability and ensure your business model is sustainable.
Different revenue streams have different characteristics. Some provide recurring income, while others are one-time transactions. Analyzing these differences will inform your overall business strategy.
Aligning Model with Your Strengths

A crucial aspect of choosing the right business model is ensuring it aligns with your strengths. A model that leverages your existing skills and resources significantly increases your chances of success. Consider your core competencies. Are you a skilled producer, a gifted marketer, or a natural networker? Choose a model that amplifies these strengths.
For example, if you excel at product development, a direct-to-consumer model or a licensing model might be ideal. If your strength lies in building relationships, consider a franchise model or a partnership-based approach.
Testing and Validating the Model
After designing a potential business model, rigorous testing is crucial. This involves validating key assumptions. Have you accurately identified your target customer? Does your value proposition resonate with them? Is your chosen revenue stream viable? Testing helps answer these critical questions.
Start with small-scale experiments. Gather feedback through surveys, interviews, and pilot programs. Analyze the data collected to understand what works and what needs adjustment. Be prepared to iterate based on the results. Flexibility is key during this phase.
Making Adjustments Over Time
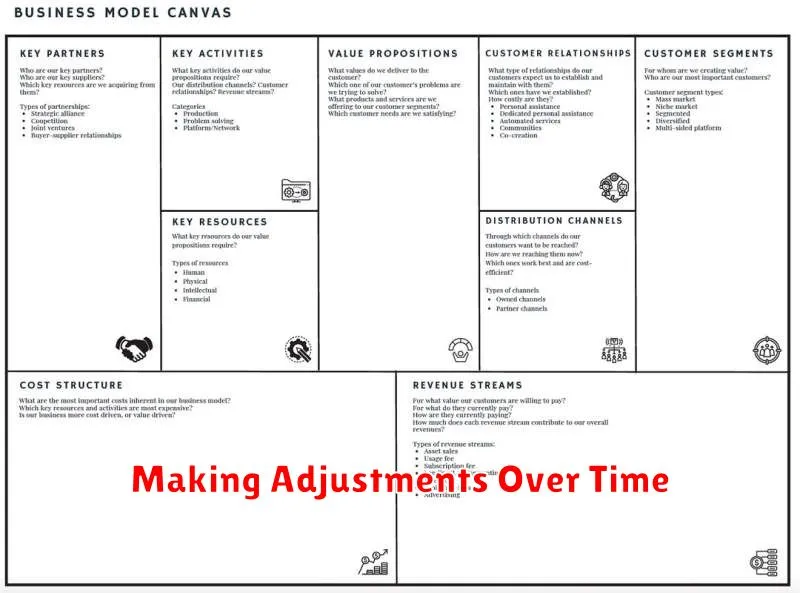
Choosing a business model isn’t a one-time decision. Market conditions, customer needs, and even your own internal capabilities evolve. Flexibility is key.
Regularly evaluate your chosen model’s effectiveness. Track key metrics like customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and revenue growth. If these metrics aren’t meeting your expectations, be prepared to pivot.
Adaptability is crucial for long-term success. This may involve tweaking your pricing strategy, expanding into new market segments, or even overhauling significant portions of your initial model. Don’t be afraid to experiment and iterate.